From Indoor 3D: Overview on Scanning and Reconstruction Methods, chapter 3.5.2.
Process
- Take two scans of 2D/3D point cloud
- Compute the center of mass and shift the point clouds on top of each other
We want to find the transformation between model set and data set . The problem is cast as a least squares minimization problem, so that we want to minimize the cost function
where for each point there is a closest point .
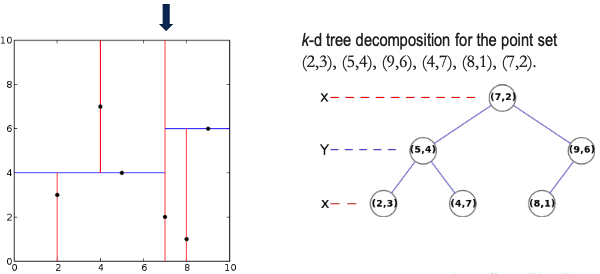
Computation of the closest point is the most computationally expensive step in ICP. Therefore, we don’t loop over all points in d to find a closest point for , but we search with optimized k-trees, .
- k-dimensional tree is a space-partitioning data structure for organizing points in a k-dimensional space
- each point of the kd tree is k-dimensional and divides the space in two for the chosen direction.
Normalize w.r.t. the center of mass of each point cloud:
Then we can rewrite the cost function as:
where
- we denote
After we rearrange the terms and raise to the power of 2, we get:
where we divided the rotation and translation!
- We want to minimize this rotation error:
- The cross-term since all values refer to centroid ⇒ and are both zero.
- The translation error has its minimum when or
Therefore, the algorithm needs to only minimize the first term, i.e.
The optimal solution is calculated by matrix factorization, using SVD (Singular Value Decomposition).
We consider the cross correlation matrix
where
- ,
- ,
contain the information of the 3D points in a stacked form