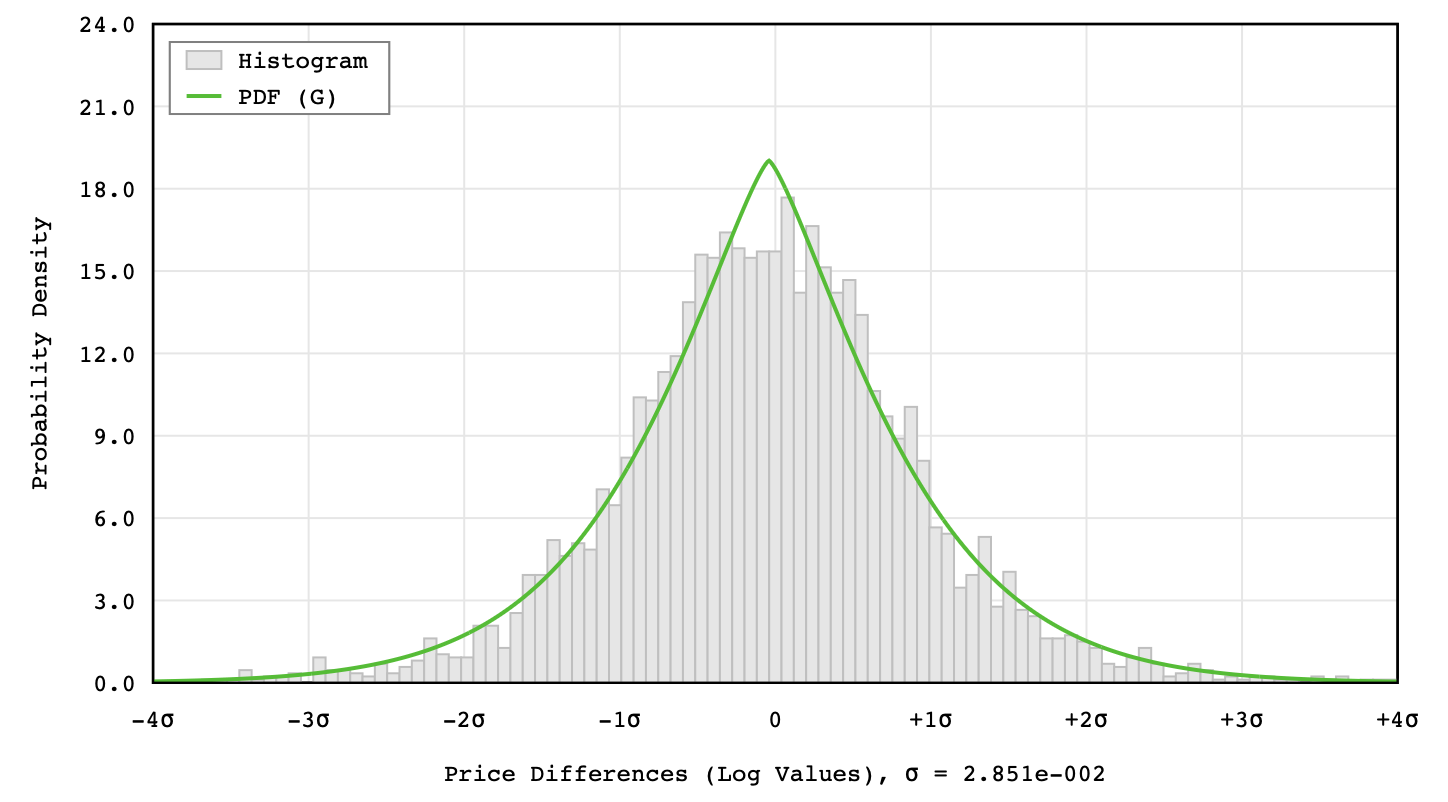
Source: https://jkillingsworth.com/2022/07/07/generalized-normal-distributions/
First encountered it in the optimal estimation subject. I had to use it to model some small uncertainty of a “softly bounded” interval of likely depths when measuring them with some prior knowledge .
Mathematically, the Standard Normal is just a specific case of the Generalized version with and .
- is the location parameter. It can be both positive and negative
- is the scale parameter. Always positive
- is the shape parameter. Always positive
The Gamma function acts as a normalization constant to ensure the total area under the probability density function PDF equals to 1.
In my case, the value adjusts the scale of the distribution based on the shape parameter β so that the probabilities remain valid regardless of how “flat” or “pointed” the curve becomes.
The generalized normal distribution can also take the form of a uniform distribution as the shape parameter approaches infinity.
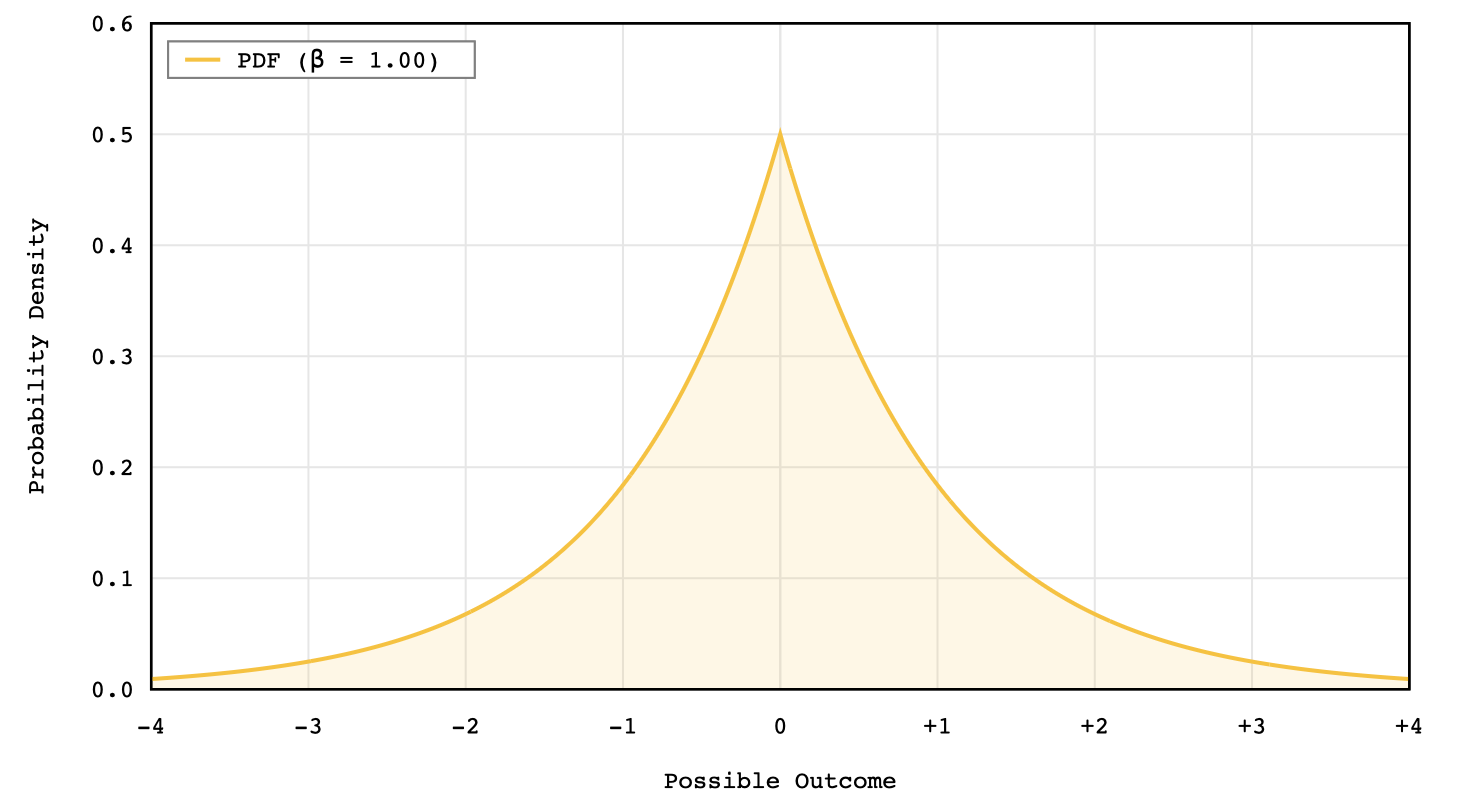
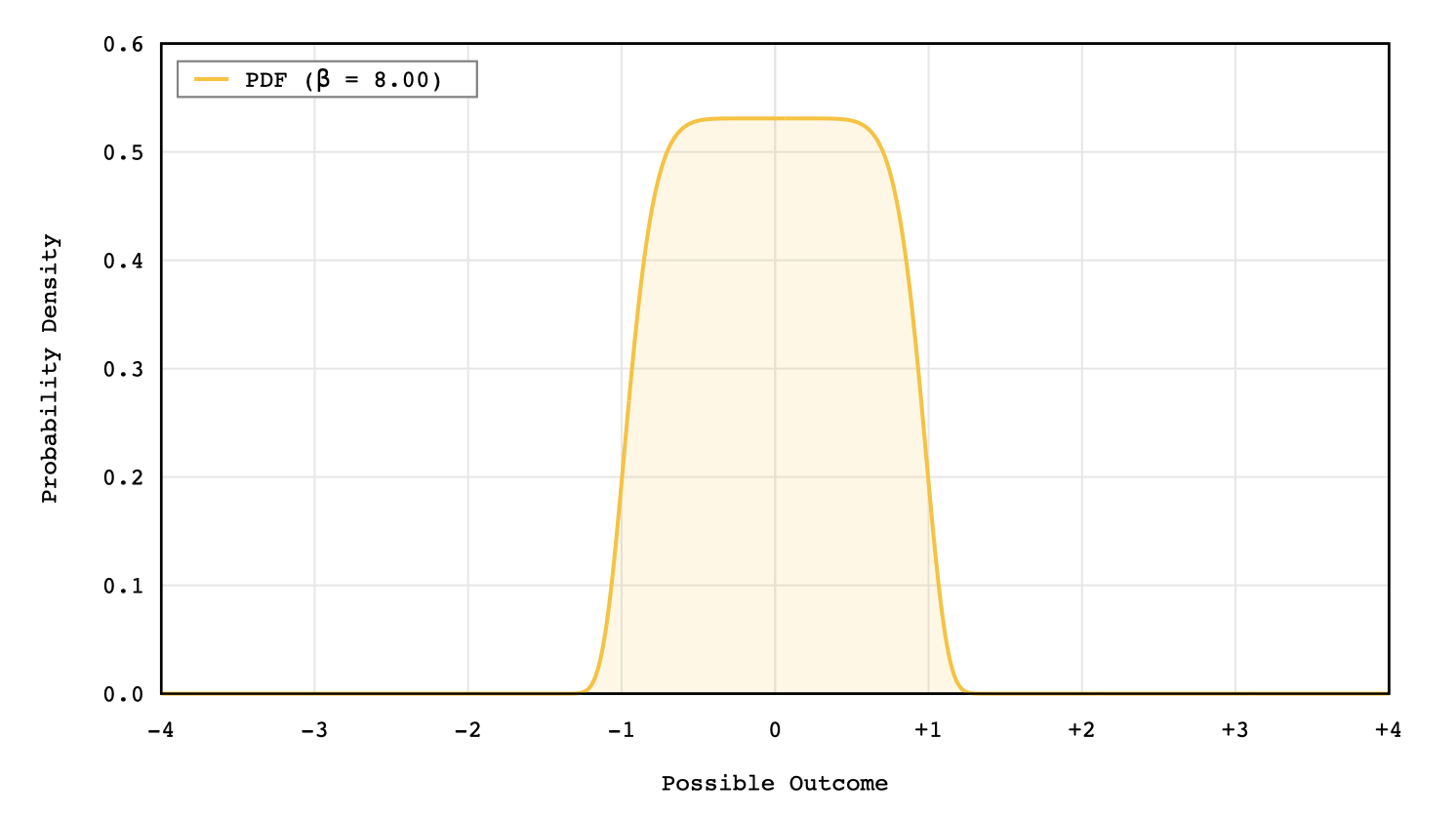
Numerical Parameter Estimation
If you have a set of observed data that is distributed according to a known probability distribution, you can use the maximum likelihood method to estimate the parameters of the distribution.
If the distribution is a normal distribution, the parameter values can be solved for analytically by taking the partial derivative of the likelihood function with respect to each one of the parameters.
To fit the generalized normal distribution to an observed set of data, we need to find the parameter values that maximize this function. Instead of coming up with an analytical solution, we can use a numerical optimization method. Taking this approach, we need to come up with a cost function that our optimization method can evaluate iteratively.
By doing this, we will be able to fit the data by finding the parameters and .