Lecture 7 from my Systems Engineering class.
Uncertainty and Margins
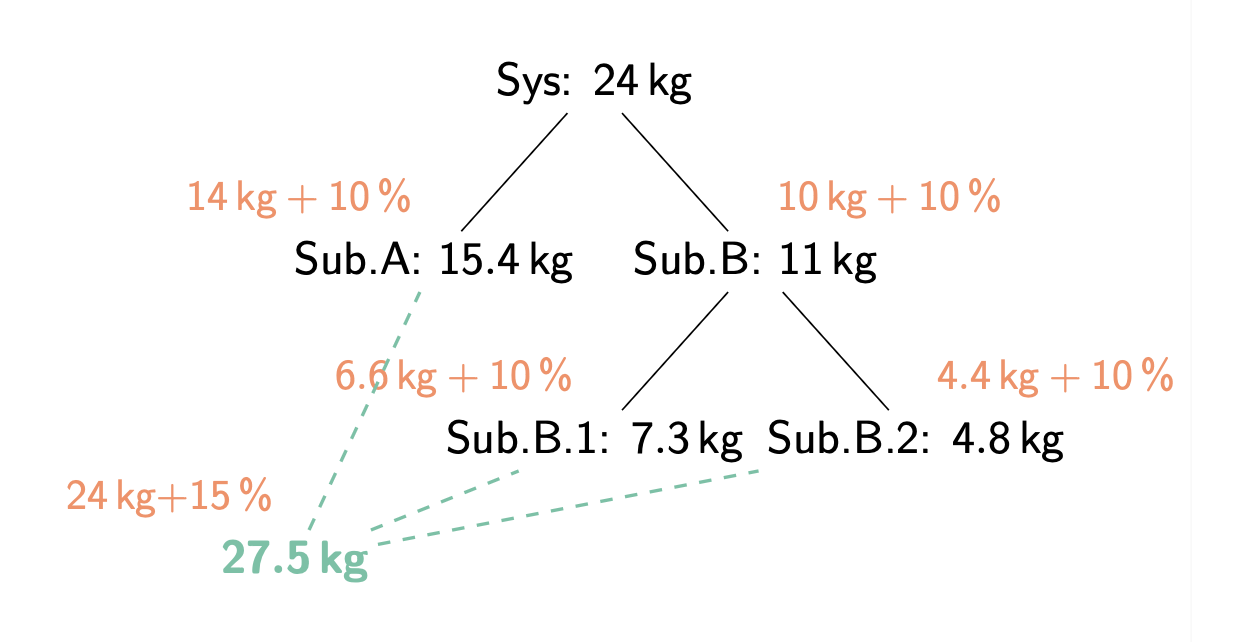
-
The margins are not repeated or assumed: be explicit.
-
Complex budgets arise because of:
- error
- bandwidth
- range
- time
-
Life-cycle costs:
- development costs
- production goods
- operational goods
- decommissioning goods
Project Management Triangle
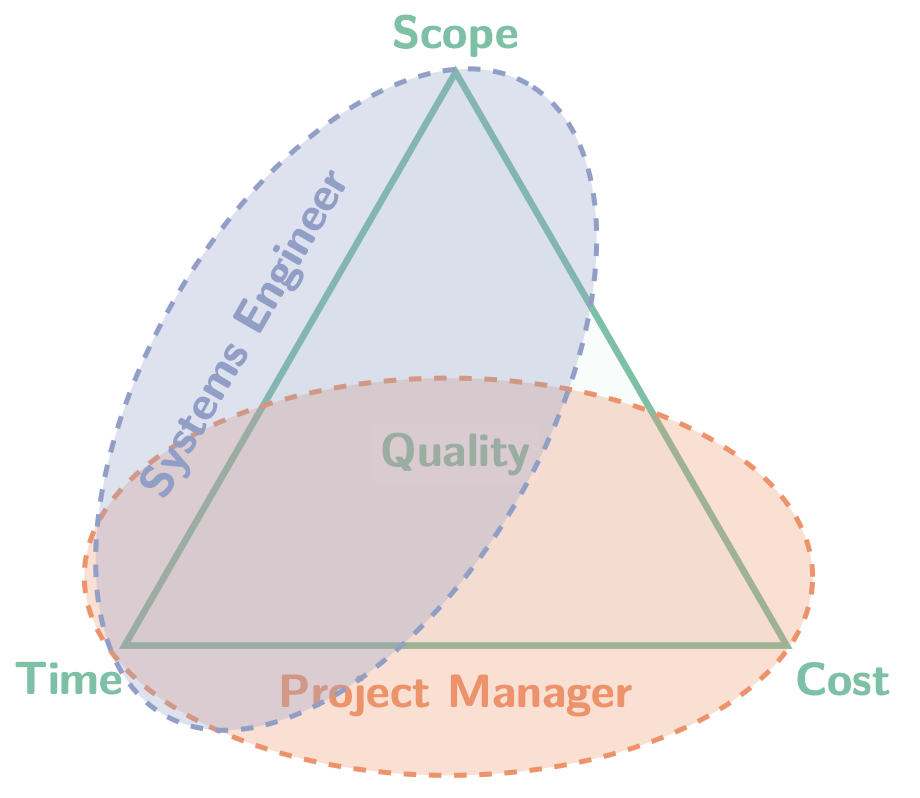
Good, fast, cheap. Choose two.
Who gets to make the decisions?
RASCI
- Responsible (does the work to complete the task)
- Accountable (reviews and approves the task)
- Supportive (helps complete the task)
- Consulted (provides input)
- Informed (kept in the loop)
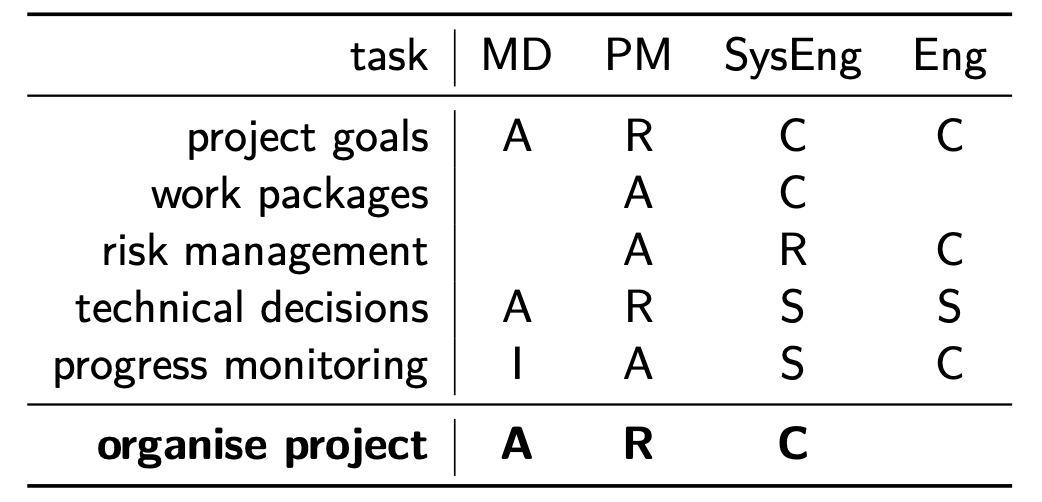
In short, the one with more responsibility makes the decisions. The PM usually has more power, but the SE has more influence.
What is the difference between accountable and responsible?
- Your head will roll vs. you must make it happen
Steps
- Define the question
- Get the options
- Evaluate
- Choose & Record
- Monitor implementation & outcome
Pugh Method
Idea: Comparing options on (weighted) criteria to select the best.
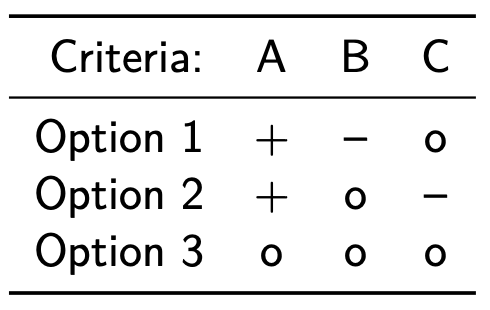
- Others include
- Decision Tree
- Belief decision matrix
- Minimax / Maximin
From Claude AI
- Decision trees: best for analyzing decisions that unfold over time where each choice leads to different branches of possibilities
- Pugh for comparative design evaluation. Good for engineering design selection where you need to systematically evaluate how different options stack up against each other on various attributes. Less focused on risk, more on relative performance.
- Decisional balance sheets for multi-stakeholder qualitative decisions. Useful for complex decisions with social, ethical, or organizational implications where you want to weigh pros and cons across different dimensions
- Maximin: for each option, you look at the worst-case scenario, then choose the option whose worst case is the best among all worst cases
- Minimax: this is used when you’re risk-averse but focused on avoiding the worst possible regret rather than the worst outcome (how badly you’d feel if you made the wrong choice)
- Belief decision matrix: this helps when dealing with uncertainty but you have some basis for estimating likelihoods, unlike minimax/maximin which assume complete uncertainty
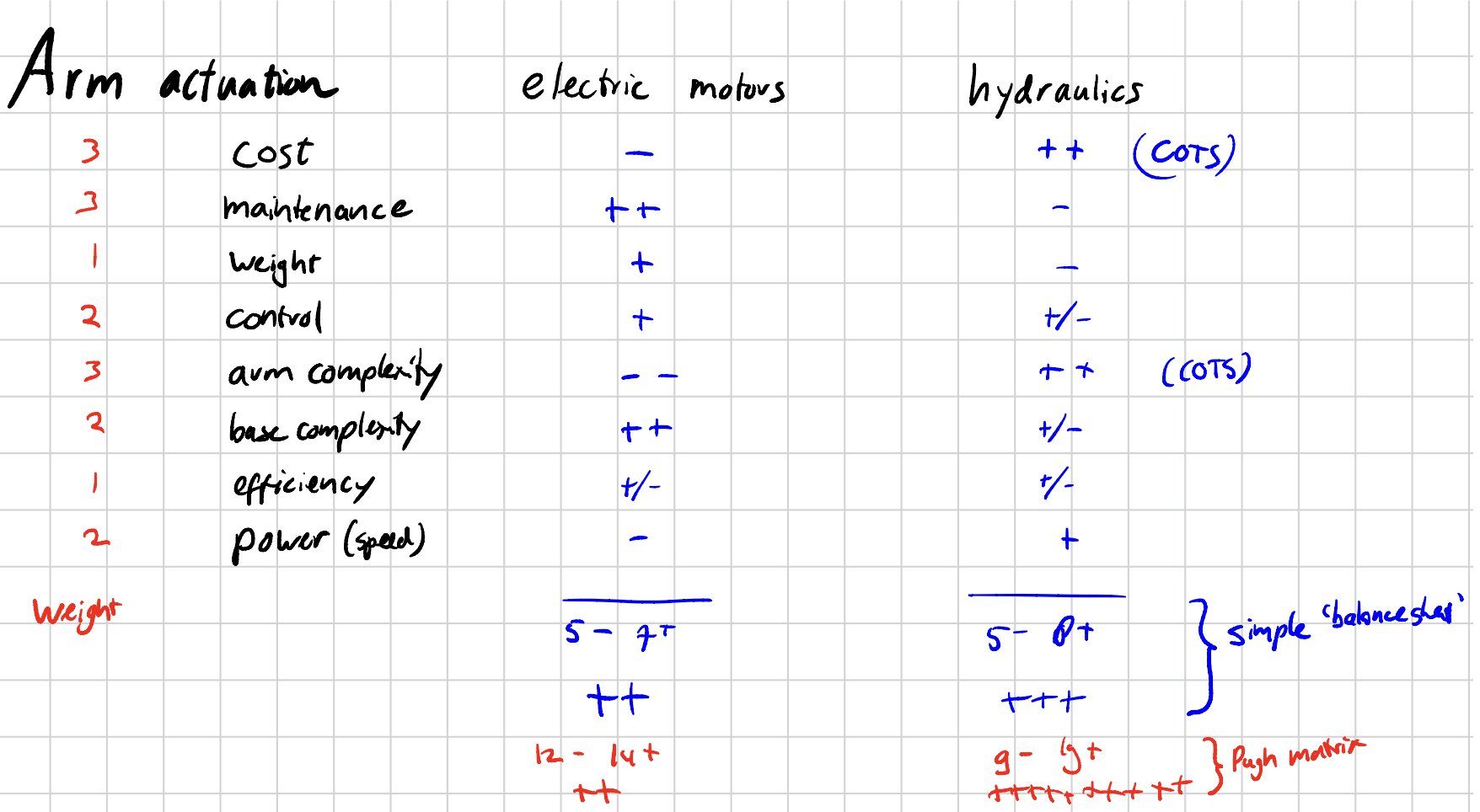
In the example above; at first glance most people would incline towards electric motors. But the sheet analysis (together with Pugh) makes it clear that hydraulics is actually better for the budget, constraints and overall attributes that we have / need.
What is scope creep?
- Slowly making the system bigger/more complex than the initial plan.
Which step of the decision-making process can be done via design space exploration?
- Getting the options